应陈渭教授的邀请,美国麻省理工学院复杂系统研究中心研究员Hilario Oh博士来我院交流并作学术讲座。欢迎感兴趣的师生届时参加讲座。
主讲人:Dr. Hilario Oh
(Research Affiliate at MIT Park Center for Complex System)
讲座题目:A Systematic Approach to Design
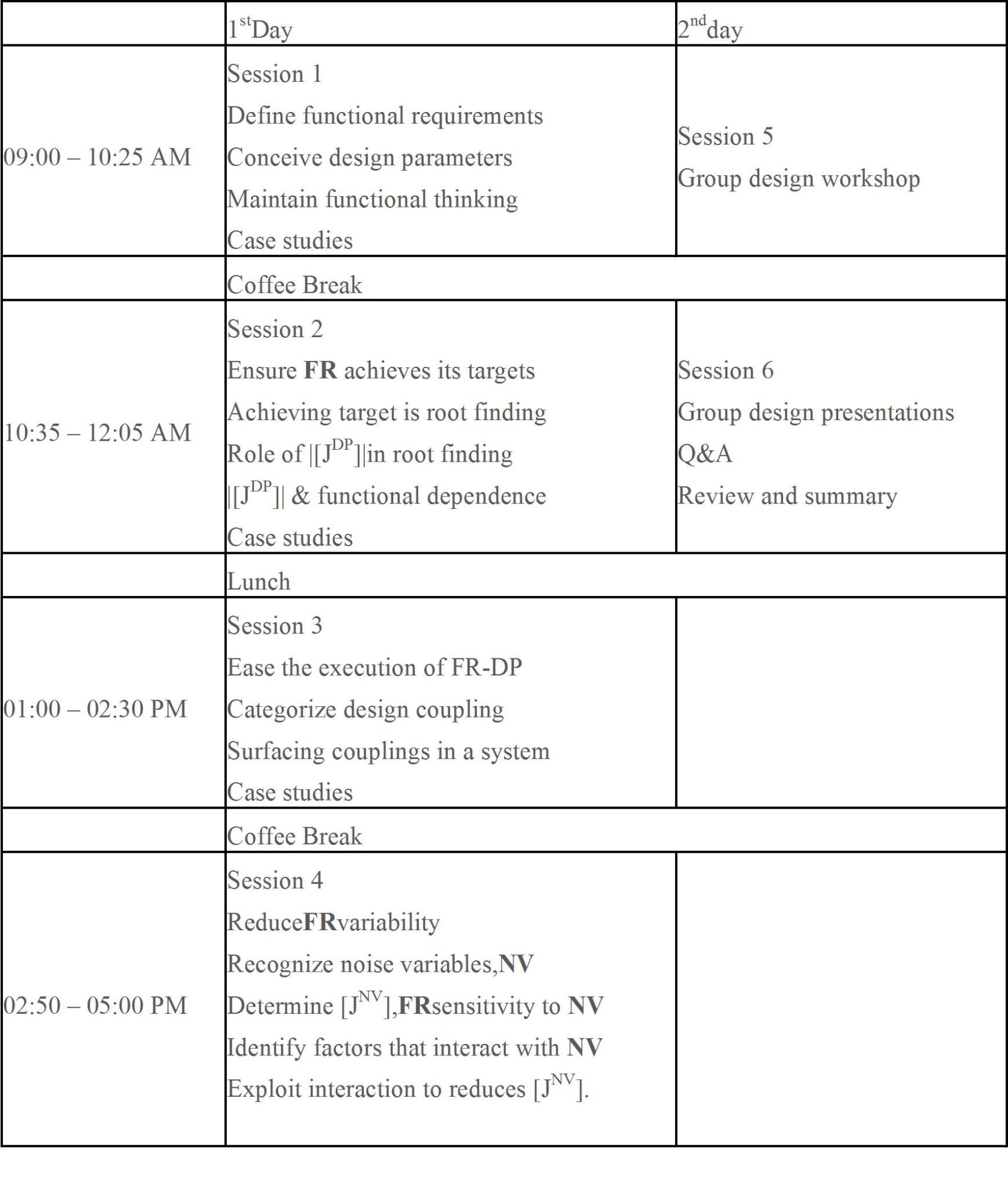
讲座时间:2017年4月3日到4月4日
讲座地点:机械学院第三会议室
讲座内容:
This course integrates Axiomatic Design (AD) and Robust Design (RD) into a unified and systematic approach to design for FR consistency and on-target performance. This course will introduce and illustrate the concepts and implementations of AD and RD with real life examples and case studies. The case studies include press-fit design for power transmission, design of ATM, hubcap design, design of ignition switch, surfacing couplings in car door to body integration, reducing complexity in track to enhance litho-track integration, setting control parameter of a crawler crane and snap-fit design.
专家简介:
Dr. Oh received his Ph. D. from University of California, Berkeley, 1967. After a year of postdoctoral fellowship at UC Berkeley, Dr. Oh joined General Motors (GM) Research Laboratories in 1969 and spent the next 19 years doing R&D in machining of brittle car components. In 1985, Dr. Oh was called into the GM Car Divisions to deal with quality crisis GM was facing, thus begun his lifelong endeavor at quality. In 1996, he joined Silicon Valley Group, a semiconductor equipment manufacturer, as Corporate Vice President in Quality and Productivity. In 1996 thru 2006, he was invited as Senior Lecturer in MIT Mechanical Department to share his industrial experience with the students. From 2006 to the present, he was associated with MIT Park Center for Complex System as Research Affiliate. Dr. Oh teaches quality methods, including robust and axiomatic design, always through real life problems and case studies.
Course Summary
Primary objective in design is to achieve the target values of the design functional requirements (FR) with reduced variation around them. Failure to achieve the objective can occur in three ways: (1) missing or incorrect definition ofFR; (2) functional dependence amongFRthat makes tuning to target values ofFRimpossible; and (3) corruption by “noise” that causes variation inFR.
The solutions are: (1) formulate the complete and rightFRthrough functional thinking; (2) simplify tuning with uncoupled design; and (3) reduce sensitivity to noise by exploiting the interaction of control and noise variables. Solutions (1) and (2) are at the core of Axiomatic Design (AD) while solution (3) is the essence of Robust Design (RD). This course integrates AD and RD into a unified and systematic approach to design forFRconsistency and on-target performance. This course will introduce and illustrate the concepts and implementations of AD and RD with real life examples and case studies.